2 1 non binding price floor.
Definition of binding price floor.
Governments usually set up a price floor in order to ensure that the market price of a commodity does not fall below a level that would threaten the financial existence of producers of the commodity.
2 basic theory in perfectly competitive markets.
More specifically it is defined as an intervention to raise market prices if the government feels the price is too low.
A price floor is an established lower boundary on the price of a commodity in the market.
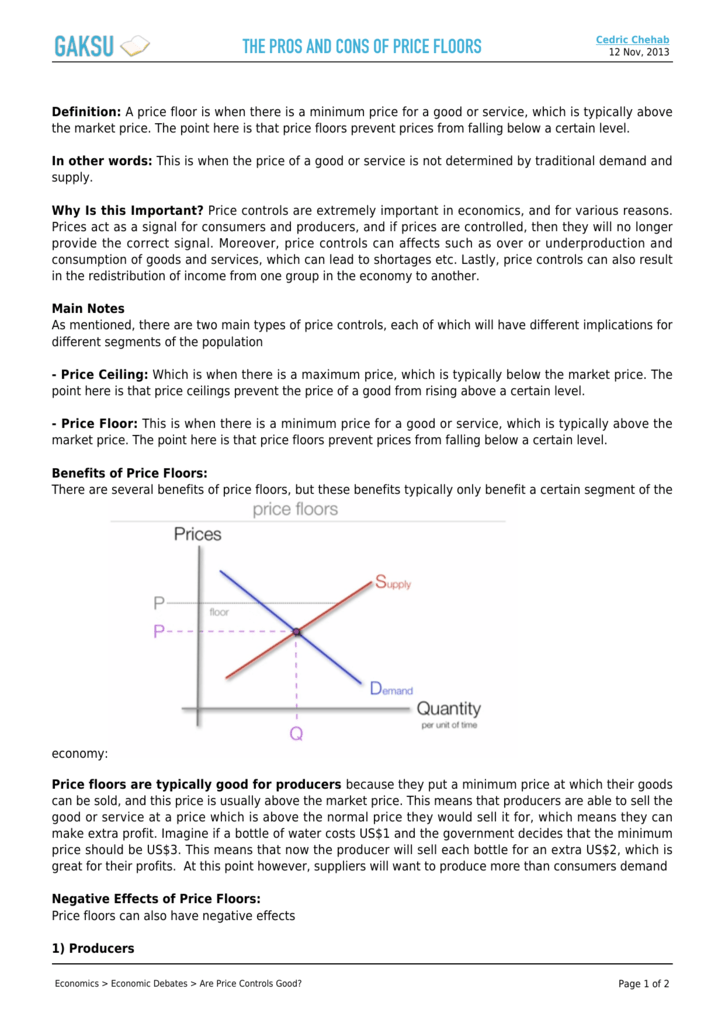
Price floors set above the market price cause excess supply.
If a rock wants to fall from an altitude of 50 meters to an altitude of 20 meters than the floor must be above 20 meters in order to be.
Where this gets tricky is that a binding price ceiling occurs below the equilibrium price.
A price ceiling is a type of price control usually government mandated that sets the maximum amount a seller can charge for a good or service.
Home equilibrium price ceilings floor supply and demand what is a price ceiling.
3 basic theory in monopsonistic markets.
A lot more mid age users are clicking on the internet iit kharagpur launches telemedicine software smaller brands may be forced to import fully built mobile devices after latest bcd levy.
Where this gets tricky is that a binding price floor occurs above the equilibrium price.
A price floor or a minimum price is a regulatory tool used by the government.
Since the 1999s the eu has used a softer method.
Examples of binding and non binding price ceilings.
While price ceilings are often imposed by governments there are also price ceilings which are implemented by non governmental organizations such as companies such as the practice of resale price maintenance.
2 2 binding price floors.
Price floors set below the market price have no effect.
A binding price floor is a required price that is set above the equilibrium price.